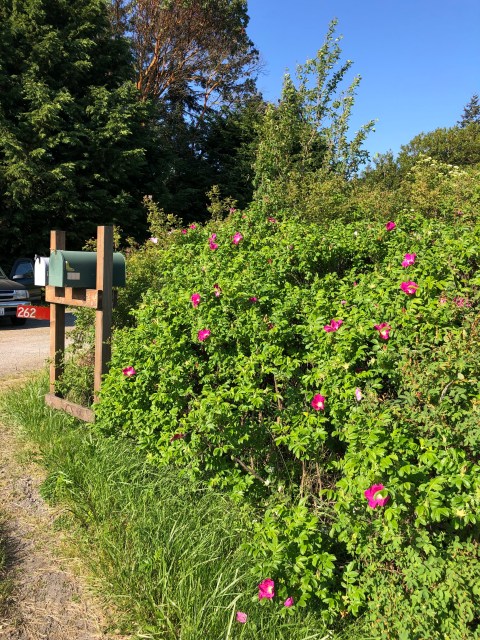
What is a Hedgerow?
A hedgerow has been described as a long, narrow forest. Or a boundary, a green fence, an enclosure for livestock, or a bio-diverse habitat between paddocks. A cultivated transition from one zone to another. The lines people have drawn across the landscape. The term itself comes from the British Isles where thickets along fields are treasured as natural habitat and historic significance. They even have their own preservation society!
Some of the hedgerows I planted in the late ‘80s are 35 years old now and I have made mistakes. The upkeep of hedgerows that are fifty-to-one-hundred years old gives me pause. Imagine a culture where a hedgerow is a respected part of the landscape—where they are planted with future generations in mind.
Robert Macfarlane wrote Landmarks, a book of terms for the cultivated and wild landscape. Although it is about the British Isles, it stirs the imagination about a language for a sense of place. By capturing these terms from an agrarian time before they are completely lost, he provides a glimpse of how people have known their land.
There is a page devoted to old terms used for hedgerows. ‘Smeuse’ refers to the gap at the base of a hedge created by the regular passage of small mammals. ‘Buckhead’ is a term for cutting the entire hedge within two-three feet of the ground and ‘bullfinch’ is a hedge that is allowed to grow tall without any ‘laying’ a horticultural technique of pruning and bending the woody thicket to keep it dense.
When I bought my property, it was enclosed with old cedar posts and barbed wire. It had been logged over and was kept mowed or perhaps grazed by a few head of cattle. Any existing hedgerow vegetation was simply where the tractor mower couldn’t get close to the fence.
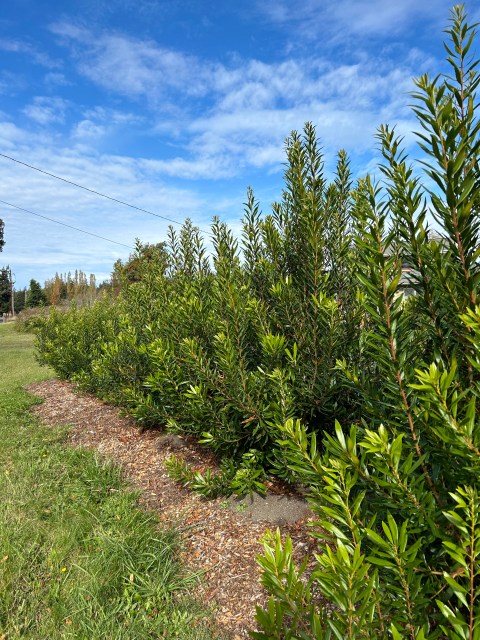
My goal in planting hedgerows was to create more privacy. I had just arrived from owning a farm in the Ozarks where we planted saplings to create a riparian corridor along a creek that tended to flood. Planting trees and shrubs seemed a natural part of caring for land. We had not heard of permaculture or agroforestry, we had wanted to plant trees for preventing erosion, and future fence posts, and habitat for wildlife.

If you are thinking of planting a hedgerow, ask yourself some questions and try to answer the best you can. What are your goals and how much time and energy are you willing to devote to the project? If you have big dreams and only little resources, phasing the project over several years will be more satisfying. If you want the hedgerow to perform too many functions, you might over burden the design.
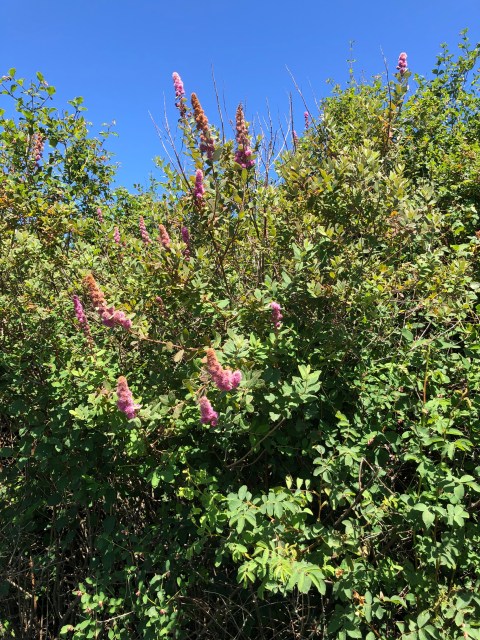
All over Jefferson County we see volunteer hedgerows that sprang up along the edges of fields. Nobody planted them, and they are thriving habitat for pollinators, birds, and small mammals.

Let’s assume your primary goal is privacy, then you can create screening or a visual barrier. By selecting mostly native plants, the hedgerow can also be pollinator-friendly, drought tolerant (once established), and provide bird habitat. If on the other hand, you want to plant hedgerows on a working farm where they will perform functions such as livestock-proof, green fences, or restore and protect degraded streams, you might want to look at the Thurston County Cooperative Extension’s Hedgerow Toolkit.
Next see: Designing a Native Hedgerow